The direct electrification of uses appears to be the most relevant solution to decarbonising the economy. In sectors where it is difficult (or even impossible), use of low-carbon hydrogen will be a key driver for achieving carbon neutrality. This is the EDF Group's strong belief.

Your browser does not support javascript.
To enable you to access the information, we suggest you view the video in a new tab.
[Jingle musical EDF]. Aujourd'hui 95 % de l'hydrogène est produit à partir d'une énergie fossile (source Adème magazine Avril 2021). Le groupe EDF investit depuis plus de 15 ans dans la production d'hydrogène bas carbone. L'hydrogène bas carbone est une solution supplémentaire pour rendre les transports longue distance plus durables. Et ça, c'est mieux pour le climat. EDF, devenons l'énergie qui change tout.
Did you say low-carbon hydrogen?
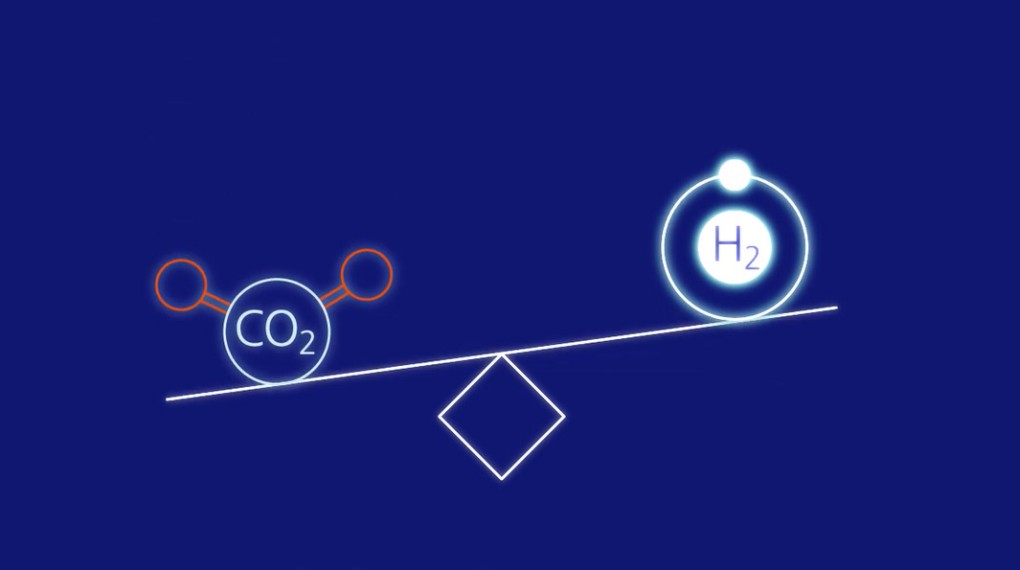
Hydrogen is a form of energy, a fuel, but also a raw material for many heavy industries such as refining, chemicals, glass, etc. Today, about 95%(1) of hydrogen is produced from fossil fuels. The process is therefore a major emitter of CO₂: to produce 1 kg of hydrogen, more than 10 kg of CO₂ are emitted.
Yet there is a way to produce hydrogen that emits a lot less CO₂: by water electrolysis, provided that the electricity used in the process is itself decarbonised. This is the case for 97% of the electricity produced in France by EDF. It is this technology that the EDF Group has chosen to rely on to produce 100% low-carbon hydrogen (≤ 3kg of CO₂ per kg of hydrogen produced).
(1) Source: ADEME Magazine – April 2021 - in French
Transcription
Hydrogen production through water electrolysis
Today, around 95% of hydrogen is produced using fossil fuels. This process generates significant CO₂ emissions: producing 1 kg of hydrogen emits 10 kg of CO₂. However, there is a way to produce hydrogen without emitting CO₂: electrolysis, provided that the electricity used in the process is itself carbon-free! This is the case for 95% of the electricity produced in France by EDF.
Your browser does not support javascript.
To enable you to access the information, we suggest you view the video Hydrogen production through water electrolysis in a new tab.


With the Hydrogen Plan, EDF is accelerating the in-depth decarbonisation of the sectors that emit the most CO₂.
Use of decarbonised hydrogen, what's the idea?
Where direct electrification of uses is still technologically difficult, if not impossible, or not economically profitable, use of decarbonised hydrogen can play a key role in achieving carbon neutrality. This is particularly the case for certain heavy industries (chemicals, refining, steel, etc.) as well as for maritime and air transport, for which e-fuels (synthetic fuels derived from electrolytic hydrogen) are a very promising way of decarbonisation. The number of projects is increasing; sustainable public support at national and European level is gradually being established. These are two strong signals that make it possible to make this future market a reality, estimated by the International Energy Agency to be worth nearly 500 Mt/year by 2050.(1)
(1) Source: Net Zero by 2050: a roadmap for the Global Energy Sector (IEA 2021)
What are the uses for decarbonised hydrogen?
EDF considers it relevant to massively expand the use of decarbonised hydrogen in industry now, to prepare for future uses in heavy transport (maritime and air) and, more in the long term, the flexibility of electrical networks.
-

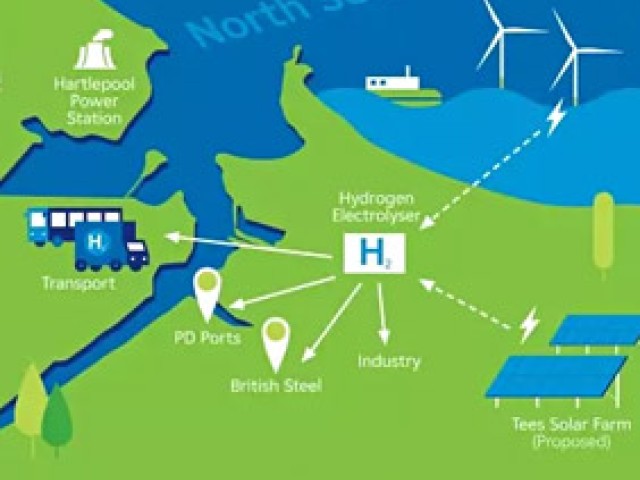
Replacing fossil hydrogen with decarbonised hydrogen in industries using hydrogen as a feedstock is the main decarbonisation solution identified for these industries: ammonia and methanol production, hydrocarbon refining and steel industry.
Starting now…Decarbonised hydrogen
in industry
-

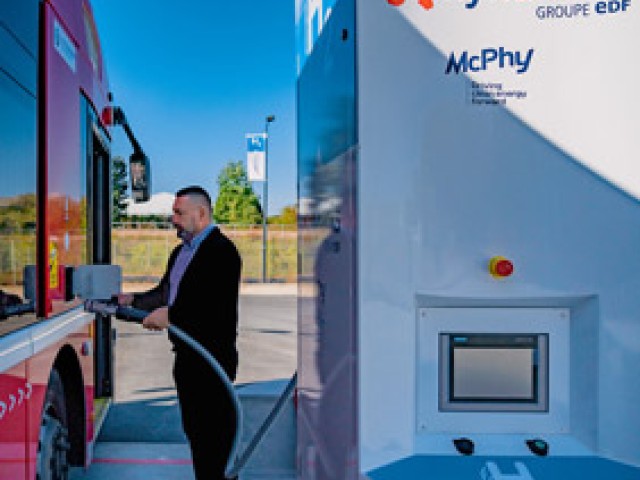
Today, local mobility projects (powering bus fleets, refuse collection vehicles, trucks) with a few MW of electrolysis have already been established in France. In the longer term, the most significant opportunities will very probably be related to the use of e-fuels, synthetic fuels derived from hydrogen (e-ammonia, e-methanol or e-kerosene) in maritime transport and aviation.
10 years from now…Hydrogen-based e-fuels
for heavy mobility
-

L’hydrogène électrolytique pourrait à terme constituer une option pour la décarbonation de la production d’électricité dans les pays disposant de peu de moyens décarbonés pilotables ou dans les petits systèmes électriques isolés.
In the longer term…Hydrogen to balance
the electrical network

Half of the CO₂ emissions to be eliminated to achieve carbon neutrality in 2050 will be achieved through innovations that do not yet exist in the market or are emerging. 100% low-carbon hydrogen is one of the solutions that EDF has decided to commit to in order to decarbonise our economy in depth


Decarbonised hydrogen and EDF... quite a story!
To achieve its ambition, EDF can rely on its long-standing expertise in electrolytic hydrogen. The first R&D work was undertaken as early as the 1970s and electrolytic hydrogen is at the heart of the expertise developed through its research institute in Germany Eifer (European Institute for Energy Research) since 2003. On the operational side, in 2018 EDF acquired a stake in the French electrolyser manufacturer McPhy to strengthen the Group's industrial expertise. Since 2019, Hynamics, a wholly owned subsidiary of the EDF Group, has been offering 100% low-carbon electrolytic hydrogen production and supply in France and Europe.
Strong assets to position itself on the entire low-carbon hydrogen value chain
-

- Nuclear and renewable energy assets in more than 20 countries
- Ability to build integrated projects
Decarbonised electricity generationEDF, the world's leading
producer of decarbonised electricity
-

- With Hynamics, a turnkey offer for the production and distribution of low-carbon hydrogen
- Engineering expertise
Hydrogen productionEngineering/Electrolysers /Operation-maintenance

-

Development of partnerships with specialised players in the production of raw materials and synthetic fuels derived from hydrogen (methanol, ammonia, e-kerosene, etc.)
Transformation of hydrogenProduction of e-fuels

-

Local presence close to the uses and support for industrial and local authority customers in their projects to decarbonise through electrolytic hydrogen
Transformation / End usesOperation of hydrogen stations

Focus on the EDF Group's emblematic low-carbon hydrogen projects and achievements
The EDF Group is developing numerous hydrogen projects mainly in Europe to decarbonise industry and the heavy transport sector. Here are a few highlights...